Modern web applications are becoming more complex and rely on an increasing number of dependencies. The larger the dependency tree is, the more likely it is to encounter version conflicts, bundle duplicate dependencies, ship unnecessary code, and negatively impact user performance.
Number of bundled dependencies
101
+114%since 2021
Number of duplicate dependencies
15
+150%since 2021
Modern web applications bundle a median of 101 direct and transitive dependencies1, an increase of 114% in the last four years.
Why the bundle contains duplicate dependencies
npm is responsible for resolving the dependency tree for the application's direct and transitive dependencies. In the case of common dependencies, when the semver query versions can not be shared, the package manager installs multiple instances to respect the package.json and avoid breaking existing functionality.
If the duplicate package is a front-end dependency, it is included multiple times in the web application bundle. This increases the size of the bundle, negatively impacts the application's web performance, and, in some cases, causes JavaScript runtime errors (ex: Duplicate React).
Resources:
Example
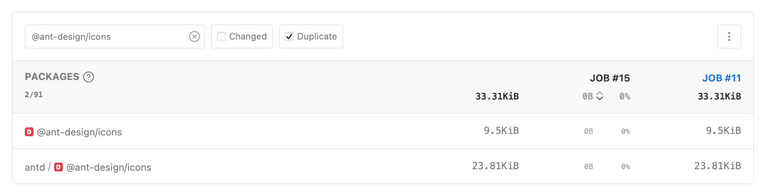
Here's an example of how the bundle can contain duplicate dependencies. In an application that depends on @ant-design/icons@4.7.0 (resolved to v4.7.0) and antd@4.24.14, npm installs two different instances of @ant-design/icons because antd@4.24.14 depends on @ant-design/icons@^4.7.0 (resolved to v4.8.1):
{ "name": "example-app", // ... package information "dependencies": { "@ant-design": "4.7.0", "antd": "4.24.14" }}npm list @ant-design/icons
example-fix-npm-dependencies@1.0.0 repo├── @ant-design/icons@4.7.0└─┬ antd@4.24.14 └── @ant-design/icons@4.8.1As a result, the bundle includes two versions of the same dependency:
How to identify duplicate dependencies
RelativeCI analyzes the bundle stats modules data, extracts the list of bundled dependencies, and identifies duplicate dependency instances. It presents the information as custom insights, metrics, and a list that you can filter and sort to discover the regressions quickly.
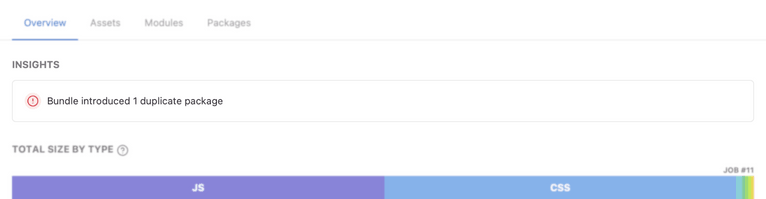
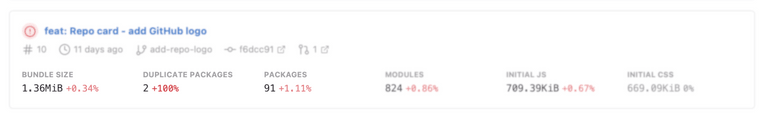
Duplicate packages insight
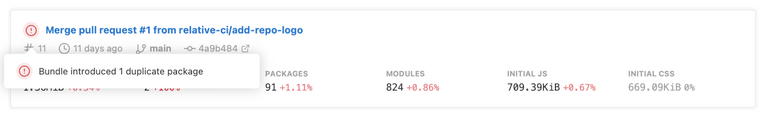
The duplicate packages insight shows the status and result of the duplicate packages analysis, allowing you to easily identify when there are regressions (new duplicate instances) or improvements (removed duplicates). The insight information is available on the bundle analysis report summary, job list, and all the integration summaries.
Duplicate packages metric
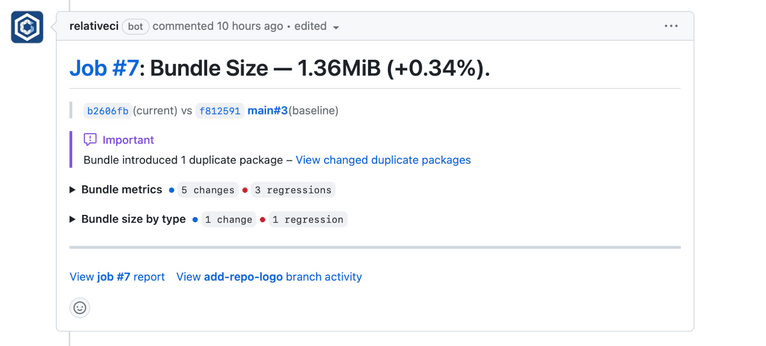
The number of duplicate packages is shown as a distinct metric on the report summary, the job list, and all the integration summaries.
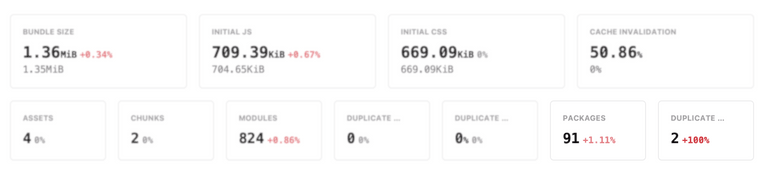
You can also use the metric as a condition on the GitHub Commit Status Review or the Slack notification.
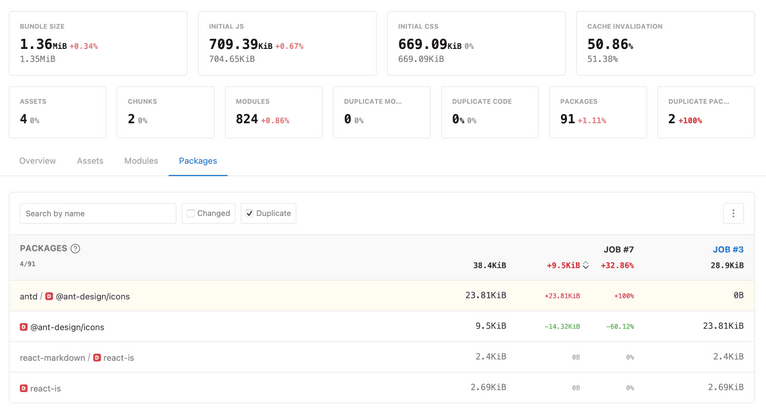
Duplicate packages data
To see the list of duplicate packages, go to the Packages section of the bundle analysis report and filter the results by the Duplicate filter. This will give you an overview of all the duplicate dependencies and their impact on the bundle size.
How to fix npm duplicate dependencies
The appropriate strategies for resolving npm duplicate dependencies may vary depending on your setup, dependencies, and versions. However, the following methods can help you eliminate duplicate packages, reduce bundle size, and enhance your application's web performance.
Run npm dedupe
npm dedupe can help quickly fix any existing issues in the package-lock.json file by flattening the dependency tree and regenerating the package-lock.json.
For example, the app dependency depends on @ant-design/icons@^4.6.0, and the correct semver resolution should be 4.8.1, though the package-lock.json resolves to 4.6.0:
npm explain @ant-design/icons
@ant-design/icons@4.6.0node_modules/@ant-design/icons @ant-design/icons@"^4.6.0" from the root project
@ant-design/icons@4.8.1node_modules/antd/node_modules/@ant-design/icons @ant-design/icons@"^4.7.0" from antd@4.24.14 node_modules/antd antd@"^4.18.6" from the root projectsRunning npm dedupe will correct the package-lock.json and remove the duplicate dependency:
npm dedupenpm list @ant-design/iconsexample-fix-npm-dependencies@1.0.0 repo├── @ant-design/icons@4.8.1└─┬ antd@4.24.14 └── @ant-design/icons@4.8.1 deduped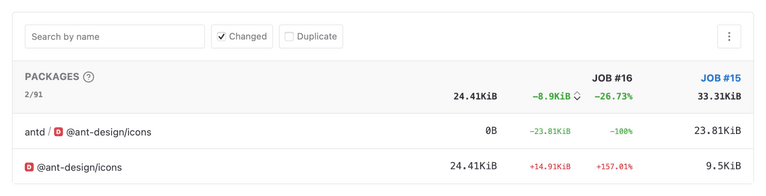
Upgrade/downgrade to a common version
Another potential solution is to update and/or downgrade the dependency to a common version that the dependents can share.
In the example above, we can update the application version to v4.8.1, the same as the version resolved for antd. npm will resolve both dependencies to v4.8.1.
npm install --save @ant-design/icons@^4.8.1example-fix-npm-dependencies@1.0.0 repo├── @ant-design/icons@4.8.1└─┬ antd@4.24.14 └── @ant-design/icons@4.8.1 dedupedUse npm overrides
The npm overrides configuration allows you to explicitly set package versions and override the npm resolution for any dependency, direct or transitive. In our example, we can override the resolved version of @ant-design/icons to 4.7.0.
Again, updating a package version, especially a major version, can break existing functionality. Remember to follow the change log of the dependency for changes, and ensure you test after updating.
{ "name": "app", /* ... */ "dependencies": { "@ant-design/icons": "^4.6.0", "antd": "^4.18.6" /* ... */ }, "overrides": { "antd": { "@ant-design/icons": "4.7.0" } }}npm list @ant-design/icons
example-fix-npm-dependencies@1.0.0├── @ant-design/icons@4.7.0└─┬ antd@4.24.14 └── @ant-design/icons@4.7.0 dedupedUse webpack configuration
Webpack allows dependency imports to be overridden at bundle time using the resolve.alias configuration option.
Don't forget that updating a package version, especially a major version, can break existing functionality. Always follow the change log of the dependency for changes and test after the update.
To point all the app imports of @ant-design/icons to the same version, we can add an entry to resolve.alias:
module.exports = { // ... webpack config resolve: { alias: { '@ant-design/icons': path.join( __dirname, 'node_modules/@ant-design/icons' ), }, },};[1]: Data based on open-source projects analyzed by RelativeCI
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Median package count | 47 | 52 | 95 | 98 | 101 |
Mean package count | 46 | 76 | 130 | 138 | 139 |